Dental Radiology
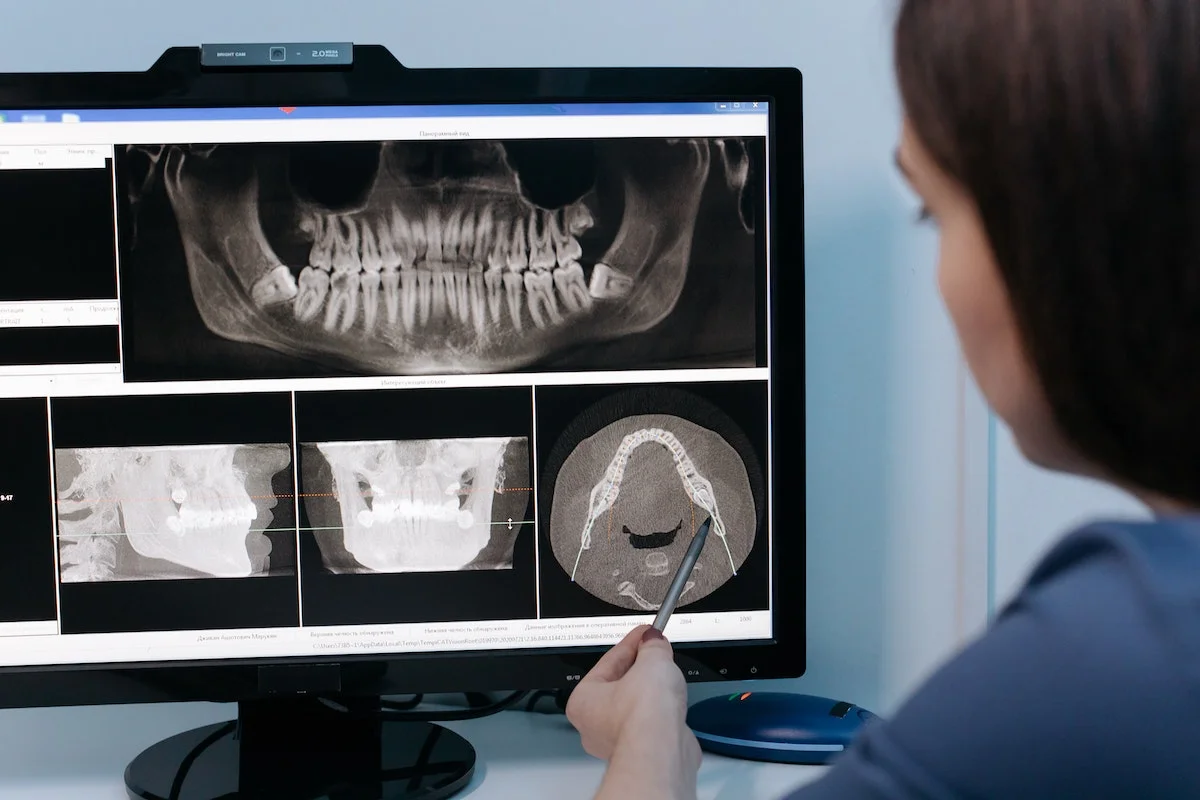
Dental radiology, also known as dental radiography, is a branch of dentistry that involves the use of radiographic imaging techniques to visualize and diagnose dental conditions. Dental radiographs (X-rays) provide valuable information about the teeth, supporting structures, and oral health that cannot be obtained through a visual examination alone. Here are some key aspects of dental radiology:
- Types of Dental Radiographs:
- Intraoral Radiographs: These are X-rays taken inside the mouth and include bitewing, periapical, and occlusal X-rays.
- Extraoral Radiographs: These are X-rays taken outside the mouth and include panoramic, cephalometric, and cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans.
- Uses of Dental Radiographs:
- Detecting Dental Caries: Radiographs help dentists identify cavities (caries) between teeth and beneath fillings.
- Assessing Tooth Roots: X-rays show the condition of tooth roots and surrounding bone, helping diagnose infections and periodontal diseases.
- Evaluating Tooth Development: Radiographs track the growth and development of teeth, especially in children and adolescents.
- Diagnosing Impacted Teeth: X-rays reveal impacted or unerupted teeth, such as wisdom teeth, which may need removal.
- Planning Orthodontic Treatment: Radiographs assist in assessing bite problems, aligning teeth, and planning orthodontic procedures.
- Detecting Oral Pathologies: X-rays aid in identifying cysts, tumors, and other abnormalities in the oral and maxillofacial region.
- Guiding Dental Procedures: Radiographs provide guidance for procedures like dental implants, root canals, and extractions.
- TMJ Evaluation: Extraoral X-rays can help evaluate the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and related disorders.
- Safety and Radiation Protection:
- Dental radiography uses low levels of radiation, and modern equipment and techniques minimize exposure.
- Lead aprons, thyroid collars, and digital sensors further reduce radiation exposure to patients.
- Digital Radiography:
- Digital X-ray technology offers immediate image results, lower radiation doses, and the ability to enhance and share images electronically.
- Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT):
- CBCT is a specialized 3D imaging technique used for detailed assessments, such as implant planning and orthodontic treatment.
- Patient Education:
- Dental professionals use radiographs to explain conditions to patients, enhancing understanding and informed decision-making.
- Interpretation and Diagnosis:
- Dentists and oral radiologists interpret radiographic images to diagnose dental conditions accurately.
- Record Keeping:
Radiographs are an essential part of a patient's dental records, tracking changes in oral health over time.


