Oral Diagnosis
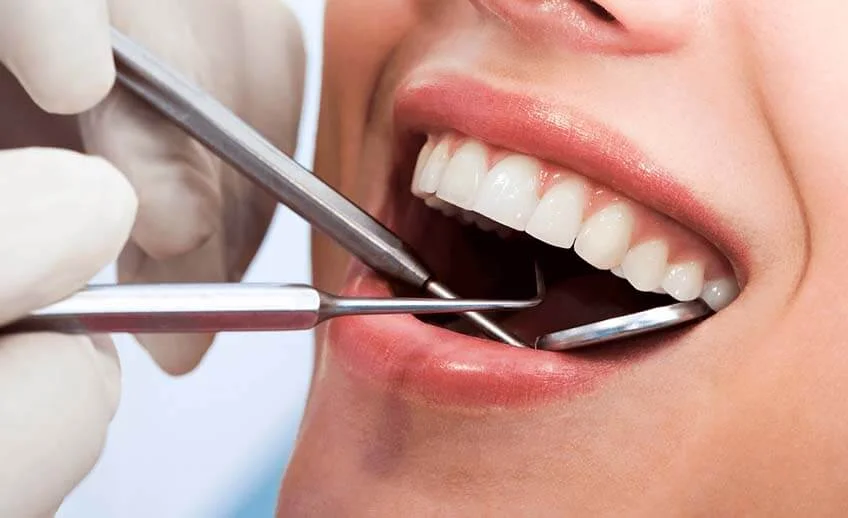
Oral diagnosis, also known as dental diagnosis, is a crucial process in dentistry that involves assessing a patient's oral health, identifying dental conditions, and creating a treatment plan tailored to their specific needs. A thorough oral diagnosis helps dentists determine the best course of action to maintain or improve the patient's oral health. Here are some key aspects of oral diagnosis:
- Patient History:
- Gathering information about the patient's medical history, dental history, and any specific concerns they have is the initial step in the diagnostic process.
- Clinical Examination:
- A comprehensive clinical examination involves visually inspecting the oral cavity, teeth, gums, soft tissues, and surrounding structures. Dentists use dental instruments, mirrors, and sometimes X-rays to assess the condition of the teeth and oral tissues.
- Radiographic Examination:
- X-rays (radiographs) provide valuable information about the teeth, bones, and structures that are not visible during a visual examination. They help diagnose conditions such as cavities, impacted teeth, and bone loss.
- Diagnostic Tools:
- Intraoral cameras and other digital imaging technologies allow dentists to capture detailed images of the oral structures, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Periodontal Assessment:
- Evaluating the health of the gums and supporting structures is essential for diagnosing and treating gum diseases (periodontal diseases).
- Caries Detection:
- Early detection of cavities (dental caries) is critical to prevent their progression. Various methods, including visual examination, probing, and radiographs, are used to assess tooth decay.
- Bite and Occlusion Evaluation:
- Assessing how the teeth fit together (occlusion) is important for diagnosing bite problems, such as malocclusions or misalignments.
- Oral Cancer Screening:
- Regular oral examinations include checking for signs of oral cancer, such as unusual lesions, growths, or discolorations.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Assessment:
- Evaluating the jaw joint and its function helps diagnose TMJ disorders and related issues.
- Diagnostic Impressions:
- In some cases, taking impressions of the teeth and jaws can help dentists plan for treatments like crowns, bridges, or orthodontic appliances.
- Digital Records and Documentation:
- Dentists maintain accurate records of diagnostic findings, treatment plans, and progress using digital charts and imaging.
- Treatment Planning:
- Based on the diagnostic findings, dentists create a personalized treatment plan that addresses the patient's oral health needs, preferences, and goals.


